Botulinum toxin and bruxism
Find out more about treatments using botulinum toxin.
Botulinum toxin treatment at natural-face
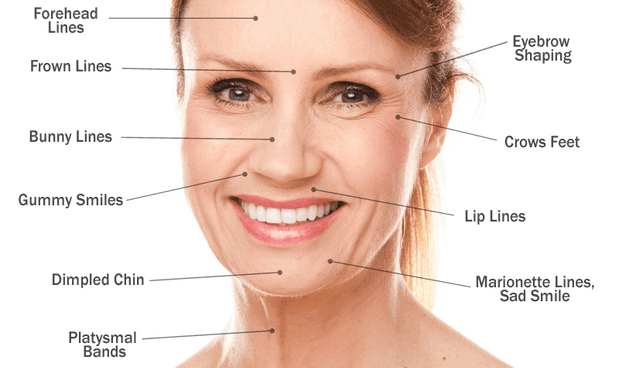
Treating facial wrinkles
Botulinum toxin type A is a highly effective substance that paralyses the muscles by blocking signals from the nerves, helping to smooth wrinkles.
The treatment is mainly used to treat facial wrinkles.
It can also be used to treat hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating).
Botulinum toxin is a protein produced by the Clostridium botulinum bacteria.
An elaborate process is used to extract and purify it for use in medical treatments.
Using a very thin needle, it is injected with great precision into the desired skin muscle.
The injection is virtually painless.
The injection procedure and preceding explanatory consultation generally take around half an hour.
You can continue with your usual activities immediately afterwards.
It generally takes two to three days for the treatment to take effect
and it lasts for an average of around three to six months.
Contraindications
Botulinum toxin should not be used by patients with a known intolerance. Treatment should also be avoided if the patient is experiencing any unusual muscle activity or inflammation in the proposed injection area.
As a precaution, botulinum toxin treatments should be avoided during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Treating hyperhidrosis
Botulinum toxin injections can be used to treat hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating), particularly in the underarm area.
For a more peaceful life
Botulinum toxin treatment for bruxism (teeth grinding)
Origin
Belgian neuroscientists first reported the use of botulinum toxin to treat teeth grinding in the “Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry” in 1990. They had a
32-year-old woman in intensive care who was in a coma following a car accident. Among other things, she was suffering from uncontrollable teeth grinding, which was destroying her teeth. Treatment with botulinum toxin was able to alleviate this almost entirely.
Research results
Since then, around 200 wider studies, individual case studies, controlled investigations and other articles have been published on the subject around the world, documenting some several thousand treatments. As early as 2000, a group of neurologists from Houston, Texas published a report on their experiences with over 240 treatments. In 2012, a Chinese research group evaluated all of these studies and carried out a meta-analysis of the results. They published their conclusions in the “International Dental Journal”. Meta-analyses are commonly used in modern medicine to gain an overview of the value and efficacy of a treatment.
Scientific conclusion
The neurologists from Houston concluded the following: “The results of this study suggest that BTX administered by skilled practitioners is a safe and effective treatment for people with severe bruxism... It should be considered only for those patients refractory to conventional therapy. Future placebo-controlled studies may be useful in further evaluating the potential of BTX in the treatment of bruxism.” Twelve years and numerous studies later, doctors at Sichuan University reached the following conclusion based on their analysis: from among the approximately 200 publications, four larger-scale studies met all the scientific standards required for a high level of validity, i.e. they were randomised, controlled studies or controlled before/after studies. These studies show that botulinum toxin injections can reduce the frequency of teeth grinding along with the pain associated with bruxism and are considered an effective treatment by patients. It is at least as effective a treatment as mouth guards and is safe and free from any side effects.
Links to studies
Contraindications
Botulinum toxin should not be used by patients with a known intolerance. Treatment should also be avoided if the patient is experiencing any unusual muscle activity or inflammation in the proposed injection area. As a precaution, botulinum toxin treatment should be avoided during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Address
natural-face
Artherstrasse 153
6317 Oberwil b. Zug
Legal


